AN-Les Poils
Hair

Hair is one of the characteristic features of mammals and has various functions such as protection against external factors, thermoregulation, production of sebum, apocrine sweat and pheromones, impact on social and sexual interactions. The hair is a derivative of the epidermis and consists of two distinct parts: the follicle and the hair shaft. The follicle is the essential unit for hair generation. It is formed by the cells of the epidermis which sink into the dermis. At the bottom of the follicle, only one epidermal layer remains: the basal layer, which gives rise to the hair.
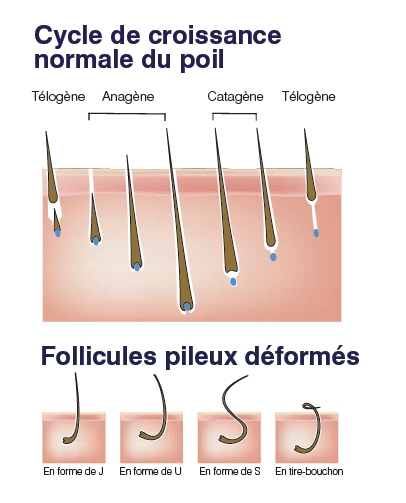
The hair follicle has a continuous sequence of growth and rest called the hair cycle. The length of the growth and rest cycles depends not only on the location of the hair but also on various factors such as age, hormone production and eating habits.
Hair growth cycle
Anagene phase
growth phase where the follicle sinks deeper into the skin as the hair grows. This phase lasts from a few weeks to six months for hair and several years for hair.
Catagene phase
transitional phase during which the bulb leaves its papilla and moves up into the skin. This phase only lasts two to three weeks for hair.
Telogene phase
is the resting period of the hair life cycle. It lasts a few months for hair.
The resting time varies widely depending on the type of hair and the nature (ethnicity) of the individual. It is important to note that a hormonal disorder or imbalance could affect the resting time. During this period, the papilla atrophies and the hair is ready to fall out, making way for the new replacement hair which is anagen.
As far as hair growth is concerned, it can be said that, in general, it lasts from five to seven years; hair on the temples and nape of the neck, from two to three years; and eyelashes, from six to eight months.
Types of hair
There are generally 3 types of hair, classified according to their texture
Vellus hair
Intermediary hair
Terminal hair