AN-Melasma vs hyperpigmentation
Melasma vs Hyperpigmentation
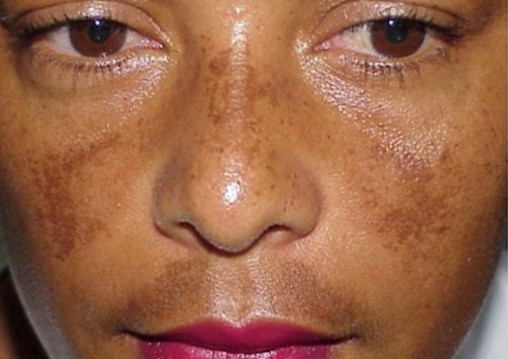
Melasma is a specific form of hyperpigmentation that commonly occurs on the face of women of childbearing age. However, not all forms of hyperpigmentation are melasma.
Hyperpigmentation vs Mélasma
Solutions
| Treating sun-induced hyperpigmentation | Treating post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation | Prevention and treatment of melasma | |
| Prevention | A minimum SPF 30+ broad spectrum should be used daily, every day of the year. | Early and aggressive treatment of the underlying cause. This may include topical, oral or injectable medications to prevent the development of the previous rash. | A minimum SPF 30+ broad spectrum should be used daily, every day of the year. |
| Topicals | Daily use of topical antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E) and retinol can help reverse some sun-induced hyperpigmentation and help prevent further pigmentation. | For acne patients, a daily routine of retinol, azelaic acid and vitamin C is helpful in minimising post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. For patients with eczema, topicals used to target pigmentation should be used with caution, as they are usually too irritating for sensitive skin. | Daily use of pigment-regulating topicals such as glycolic acid, vitamin C, retinol, azelaic acid, kojic acid, niacinamide and/or tranexamic acid can help minimise melasma. |
| Chemical peels at the institute or at home | This is the only form of hyperpigmentation where more aggressive chemical peels are beneficial. | These should be carried out under the guidance of experts. Overly aggressive chemical peels can aggravate post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. | These should be carried out under the guidance of experts. Chemical peels that are too aggressive can aggravate melasma. |
| Laser | Intense Pulsed Light Therapy (IPL) is effective in treating the widespread redness and pigmentation that occurs with sun-induced hyperpigmentation. It is only suitable for fair skin. | Soft lasers such as microsecond and picosecond lasers can improve post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. These should be performed with an expert as the wrong laser can create burns, scarring and/or additional post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. | A range of low energy laser devices can be used to improve melasma, but lasers should be used with caution as melasma can be made worse by light and laser is a form of light. |
| Oestrogeen level controls | Switching to a non-estrogenic contraceptive may result in some improvement, although it may not lead to resolution of melasma. As different contraceptives have varying effectiveness, side effects and benefits, this decision should be made with the advice of your gynaecologist and dermatologist based on your specific skin problems and reproductive goals. | ||
| Oral therapy | For severe melasma, oral tranexamic acid can be very effective, but there are potential side effects. The risks and benefits should be discussed with your dermatologist. |